Non-Max Suppression
Introducing NMS
Non Maximum Suppression (NMS) is a technique used in numerous computer vision tasks. It is a class of algorithms to select one entity (e.g., bounding boxes) out of many overlapping entities. We can choose the selection criteria to arrive at the desired results. The criteria are most commonly some form of probability number and some form of overlap measure (e.g. Intersection over Union).
Most object detection algorithms use NMS to whittle down many detected bounding boxes to only a few. At the most basic level, most object detectors do some form of windowing. Thousands of windows (anchors) of various sizes and shapes are generated.
These windows supposedly contain only one object, and a classifier is used to obtain a probability/score for each class. Once the detector outputs a large number of bounding boxes, it is necessary to filter out the best ones. NMS is the most commonly used algorithm for this task.
The Intersection over Union (IoU) metric, also referred to as the Jaccard index, is essentially a method used usually to quantify the percent overlap between the ground truth BBox (Bounding Box) and the prediction BBox. However, in NMS, we find IoU between two predictions BBoxes instead.
Implementation of IoU in Python
We are given two boxes, box1 and box2, both defined by two coordinate tuples: (x, y) and (a, b) The first tuple is the lower left coordinate, and the second tuple is the upper right coordinates.
So the area of each bounding box is as follows:
area = (a-x) * (b-y)
Now we need to find the intersection box. To do that, find the largest (x, y) coordinates for the start of the intersection bounding box and the smallest (x, y) coordinates for the end of the intersection bounding box.
# box1 (x1,y1) (a1,b1)
# box2 (x2,y2) (a2,b2)
area1 = (a1-x1)*(b1-y1)
area2 = (a2-x2)*(b2-y2)
xx = max(x1, x2)
yy = max(y1, y2)
aa = min(a1, a2)
bb = min(b1, b2)
So the intersection BBox has the coordinates (xx,yy) (aa,bb). Now we compute the width and height of the intersection bounding box, and use it to calculate the intersection area:
w = max(0, aa - xx)
h = max(0, bb - yy)
intersection_area = w*h
Now we find the union area of box boxes and compute the ratio of overlap between the computed bounding box and the bounding box in the area list
union_area = area1 + area2 - intersection_area
IoU = intersection_area / union_area
The NMS Algorithm
Input
We get a list P of prediction BBoxes of the form (x1,y1,x2,y2,c), where (x1,y1) and (x2,y2) are the ends of the BBox and c is the predicted confidence score of the model. We also get overlap threshold IoU thresh_iou.
Output
A list of filtered prediction BBoxes
Pseudo Code
- Initialize empty list $K$ for return values
- Select prediction $S$ with the highest confidence score from $P$, and append it to $K$
- Compare prediction $S$ with all predictions present in $P$ by calculating the IoU of $S$ with every prediction $P$. If the IoU is greater than the threshold thresh_iou for any prediction T present in P, remove prediction T from P.
- If there are still predictions left in P, then go to Step 1 again, else return the list keep containing the filtered predictions.
Code implementation
Lets define our function, and write the first few lines which will extract the coordinates and confidence scores for every prediction box present:
def non_max_suppression(P: torch.tensor, iou_thresh: float):
x1 = P[:, 0]
y1 = P[:, 1]
x2 = P[:, 2]
y2 = P[:, 3]
scores = P[:, 4]
Now we calculate the area of all BBoxes, and initialize our list $K$ for the return values:
areas = (x2-x1) * (y2-y1)
order = scores.argsort()
K = []
Now we begin to iterate over our BBoxes, beginning with step 2 from above by extracting the index of the prediction with the highest score.
while len(order) > 0:
idx = order[-1]
K.append(P[idx])
order = order[order: -1]
Now we get the coordinates according to the indicies by order using Torch.index_select
xx1 = torch.index_select(x1,dim = 0, index = order)
xx2 = torch.index_select(x2,dim = 0, index = order)
yy1 = torch.index_select(y1,dim = 0, index = order)
yy2 = torch.index_select(y2,dim = 0, index = order)
Now we find the intersection of the BBox S and all the predictions left in P
xx1 = torch.max(xx1, x1[idx]) # essentially max(S.x1, T.x1)
yy1 = torch.max(yy1, y1[idx])
xx2 = torch.min(xx2, x2[idx])
yy2 = torch.min(yy2, y2[idx])
w = xx2 - xx1
h = yy2 - yy1
# Clip lower bound at 0 to avoid negative values
w = torch.clamp(w, min=0.0)
h = torch.clamp(h, min=0.0)
Finally, we calculate the IoU between $S$ and all other BBoxes in $P$
intersect = w*h
rem_areas = torch.index_select(areas, dim = 0, index = order)
union = (rem_areas - inter) + areas[idx]
IoU = inter / union
# keep the boxes with IoU less than iou_thresh
mask = IoU < iou_thresh
order = order[mask]
Experiment
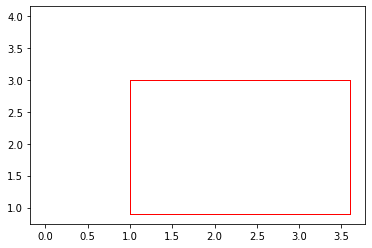
Given
P = torch.tensor([
[1, 1, 3, 3, 0.95],
[1, 1, 3, 4, 0.93],
[1, 0.9, 3.6, 3, 0.98],
[1, 0.9, 3.5, 3, 0.97]
])
we can plot the BBoxes to get this:
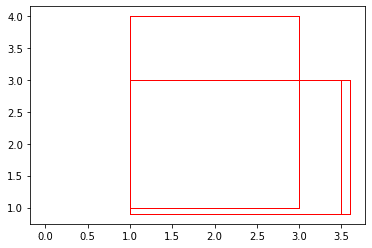 Now we run our function with iou_thresh as 0.5:
Now we run our function with iou_thresh as 0.5: